Editors’ Choice
2020 Skyscraper Competition
Anni Cai, Jinwei Hu
China
Due to human activities, the global temperature continues to rise, and Australia will enter a dry wildfire season each spring and autumn. However, Australia is facing an extremely hot year in 2019. The continuous high temperature and drought have caused drought to detonate in September. The fire, which quickly expanded and spread to other states, caused a rapid decline in air quality, devastated millions of hectares of land, and claimed the lives of hundreds of millions of animals and plants. A series of effects even lead to the irreversible extinction of endangered organisms.
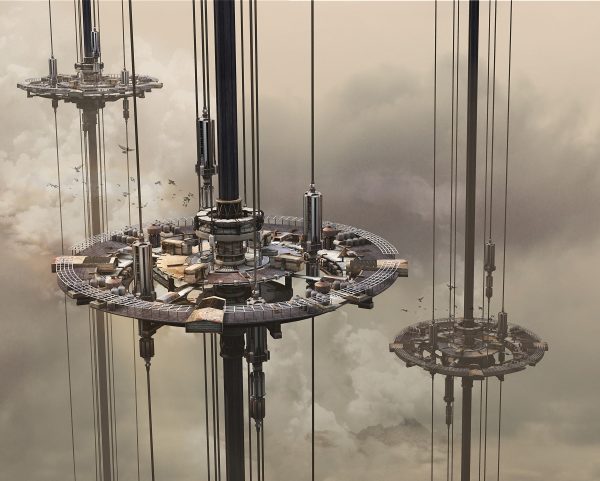
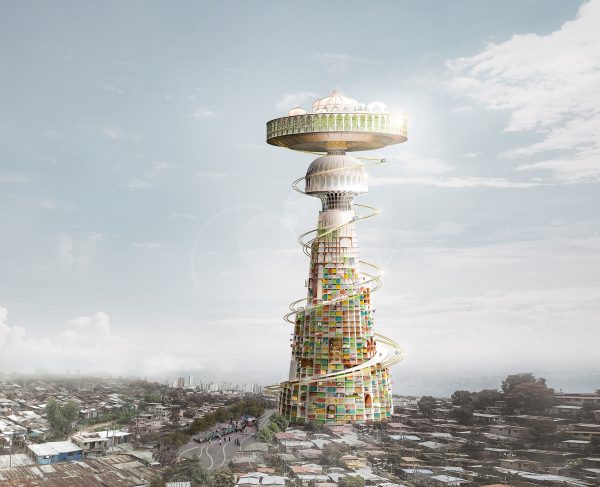
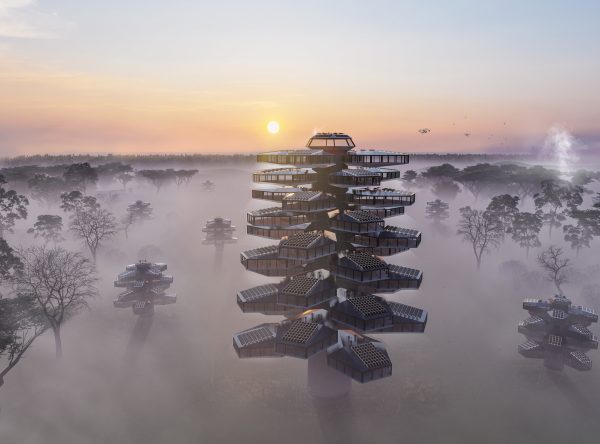
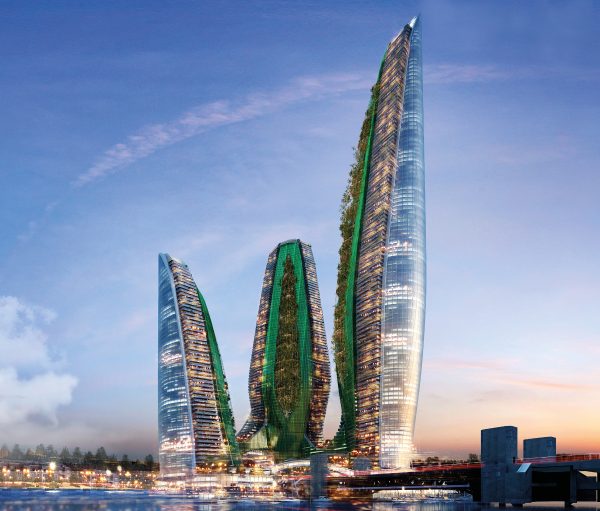
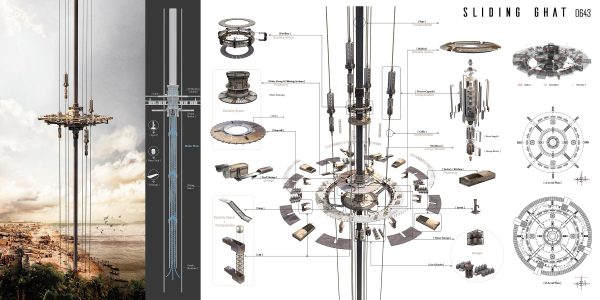
The skyscrapers are located in the Gondwana Rainforest on the border between New South Wales and Queensland, Australia, including rainforests that have never been disturbed by humans and reformed rainforests. About 200 species of rare and endangered flora and fauna inhabit it. Significant biodiversity is of great significance to world scientific research and the protection of animals and plants. The site of the skyscraper can share, protect, and study this endangered variety of rain forests and ecosystems. It can quickly rescue the endangered animals and plants in the vicinity of the disaster and increase the possibility of animal and plant heritage.
The way skyscrapers protect animals and plants stems from the story of Noah’s Ark. When disaster strikes, they can save endangered animals and plants and preserve the genes of endangered organisms. The idea of a construction robotic arm is derived from the legs of arthropod insects. The robotic arm makes the building mobile and carries endangered creatures when disaster strikes, satisfying the function of escape. Read the rest of this entry »