2024 Skyscraper Competition
Frank Hao Xinyang, An Ran
Hong Kong
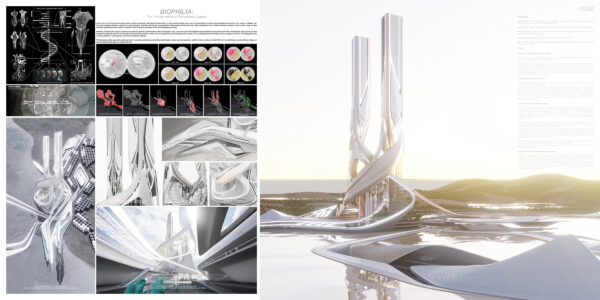
In the 30 years following the discharge of radioactive water from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Plant into the ocean, it has become evident that the impact of radioactive contamination on nature far exceeded initial estimates. Ecosystems have suffered greatly, with several species facing the threat of extinction. Humanity’s impact on nature has been more severe than imagined. Radioactive contaminants in the oceans and soil have had a long-term and widespread impact on the biosphere, leading to a global reassessment of environmental policies and a surge in technological innovations. These circumstances have compelled the scientific community and environmental organizations to seek innovative solutions to repair the environment and prevent future disasters. With advancements in genetic engineering and radioactive experimentation technology, new hope has risen from the ruins of the disaster.
Post-Fukushima Ecological Awakening
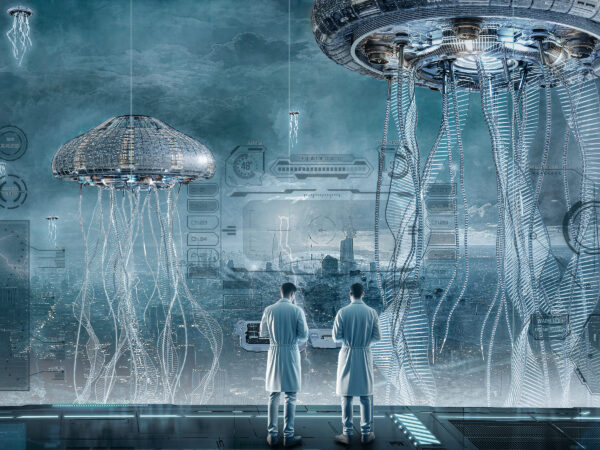
It is on this land, once heavily damaged, that a remarkable fusion of building technology, genetic engineering, and nature has taken place.
Scientists, through breakthroughs in gene transference and radioactive experimentation techniques, have decoded the secrets of certain plants and insects that thrive in radioactive environments. They have successfully used the genes of these organisms to create new giant plant species. These plants are robust enough to grow in contaminated soil and have unique physiological mechanisms to absorb and transform radioactive elements, thus reducing environmental contamination.
Building Ecological Sanctuaries
These unprecedented plants have begun to play a crucial role in restoring ecological balance in contaminated areas.
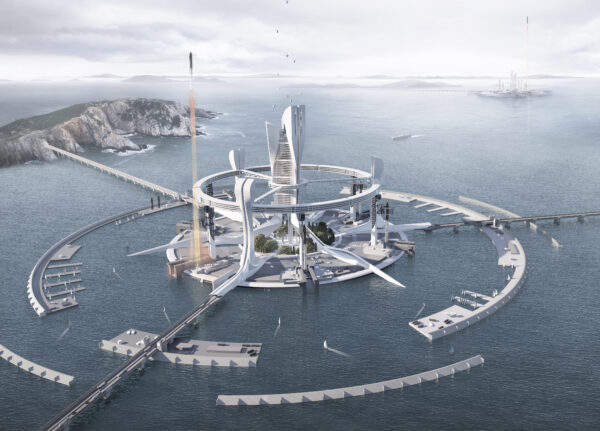
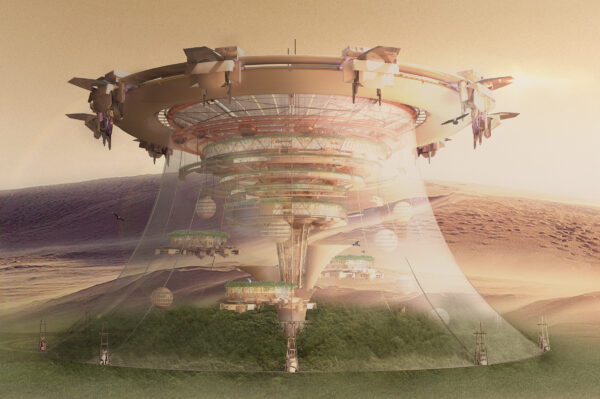
These giant plants serve not only as natural purifiers but also as shelters for post-disaster life and recovery, with their internal spaces designed for human habitation. Within these ecological megastructures are spacious living areas, efficient laboratories, and verdant relaxation spaces. In these natural sanctuaries, people can conduct scientific research, explore further environmental restoration technologies, and rediscover ways of harmonious coexistence with nature. This has led these regions to gradually become exemplars of human-nature symbiosis.
Symbols of Sustainability and Legacy
These novel plants have formed a unique ecosystem around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, known as the “Radiation Biosphere.” Here, plants and wildlife depend on each other, creating a delicate yet stable ecological equilibrium. Scientists have established a range of research facilities and living quarters within this biosphere, where environmental exploration and monitoring occur in harmony with nature, composing a magnificent symphony of life.
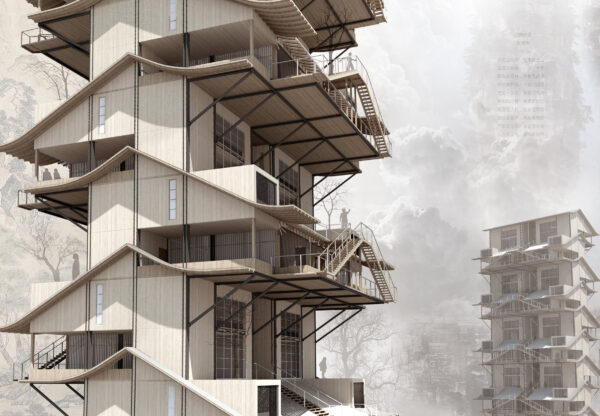
After decades of growth and evolution, these giant plants eventually fulfill their life’s mission. At the end of their life cycle, they undergo a special process that solidifies their structure, transforming them into durable building materials.
Calcified plants are carefully crafted into various types of structures, including homes, research laboratories, art galleries, and monuments. Designers have used these special building materials to create unique architectural styles and forms, integrating the beauty of technology and nature into the architecture, embodying the concept of harmonious coexistence between humans and nature.
These “buildings” are not only places for human habitation but also symbols of the post-Fukushima era’s environmental and human symbiotic philosophy.
Every building transformed from these giant plants stands as a memorial to the past and a warning for the future.
Future Outlook and Sustainable Development
This project represents a proactive response and exploration of humanity’s environmental challenges. It showcases the harmonious coexistence between humans and nature and provides a new model and inspiration for future sustainable development. In this new ecosystem, humans and nature progress together, exploring and creating a more beautiful and sustainable living space for the future. This project will inspire continued investment in environmental protection and technological innovation, creating more possibilities for the future of humanity and the planet.